BPMN Level 1 Palette
part 1 - getting started
BPMN Basics: Flow Nodes
-
Activity
-
Task (atomic) or
-
Subprocess (compound)
-
-
Event
-
Start
-
End
-
Intermediate
-
Boundary
-
-
Gateway
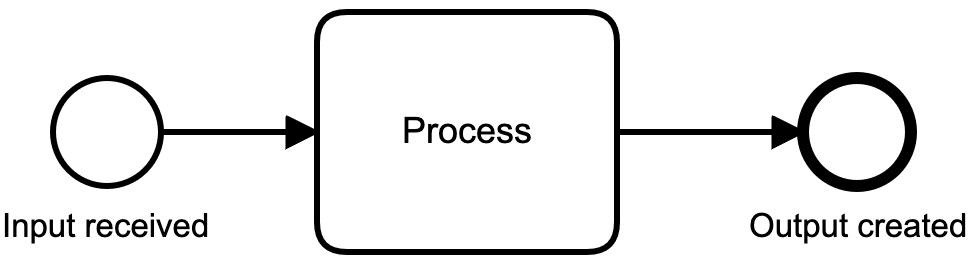
Sequence Flow
-
Describes control flow between flow elements in a process
-
Has exactly one source and one target flow element
-
Can be conditional or non-conditional
-
Can enter event or activity from any angle
-
Cannot pass a (sub) process boundary
-
Not used between pools![1]
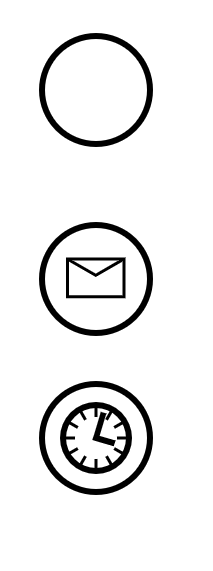
Start Event
-
Starts a process or subprocess
-
None start event - internal trigger
-
Message start event
-
Start event matched with specific message (name)
-
Useful if there are multiple ways to start a process
-
-
Timer start event
-
Process started based on time condition (moment or cycle)
-
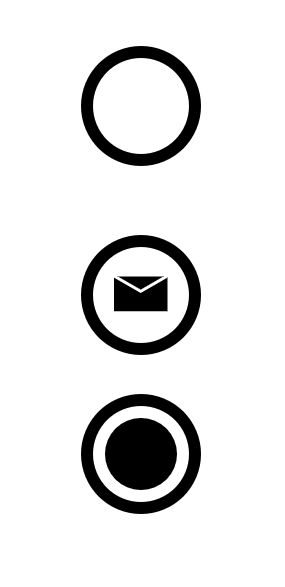
End Event
-
Ends a path within a process or subprocess
-
None end event - no emission
-
Message end event
-
End event that emits message
-
-
Terminate end event
-
Ends the (sub)process and terminates any parallel paths
-
Abstract Task
-
Activity that is atomic (not a subprocess), but unspecified (abstract[2]) w.r.t. its implementation
-
Can be automated
-
Can be manual
-
-
Often used for high level process models during initial design
-
Not meant for executable models
User Task
-
Atomic activity for execution by a human participant
-
Execution of the process path stops as the user task is created
-
Execution path continues after the user indicates the task has been completed
-
Creation, notification and "sending" information to the task is implicit in activity
-
Not necessarily an atomic action
-
User may be required to perform multiple actions
-
Service Task
-
Activity that uses a service when performed
-
Most typically used for modelling automated execution by a service external to the process engine
-
There is no manual action needed before it can start
-
The service can be invoked immediately and the task may wait for the reply
-
A request to invoke the service can be issued[3]
-
-
Execution continues after the service has been used
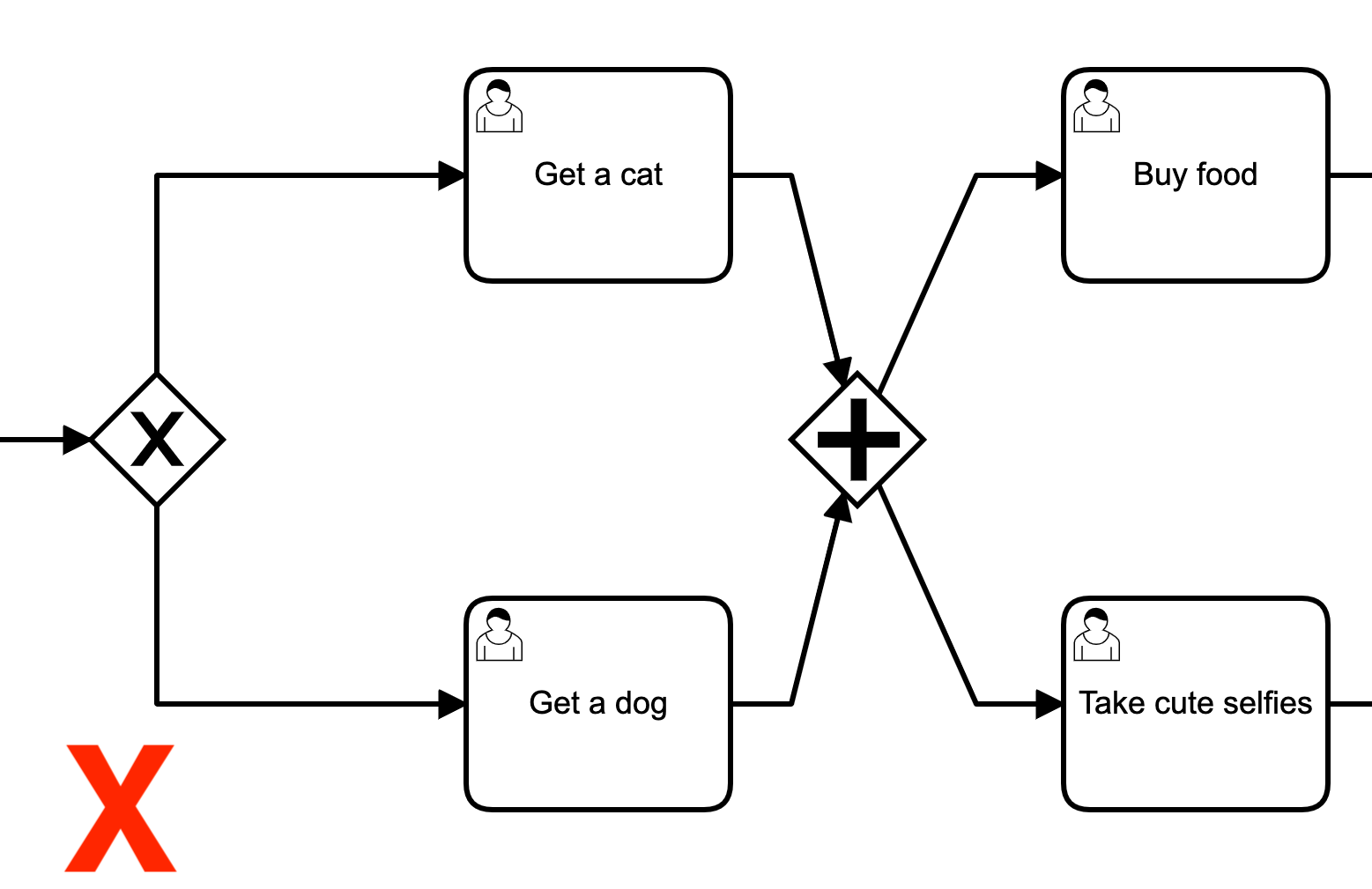
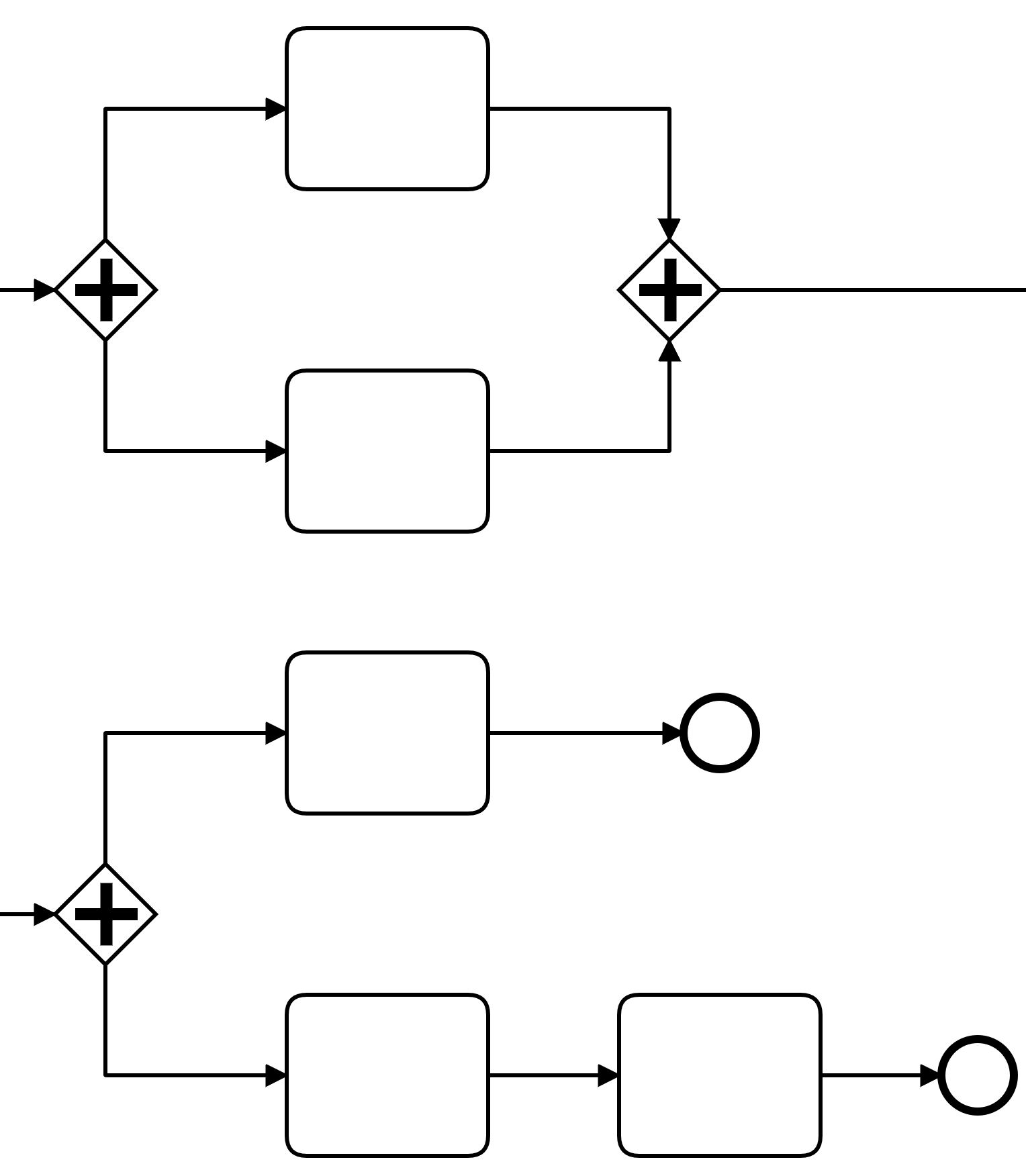
Parallel Gateway
-
Handles unconditional parallel flows
-
Splitting behaviour
-
Gateway splits incoming flow into all outgoing flows
-
-
Merging behaviour
-
Gateway merges incoming flows into outgoing flow
-
Proceeds only after all flows have reached gateway
-
All incoming paths must therefore be enabled!
-
-
Paths must not not be merged
-
But all must reach end event to end process
-
-
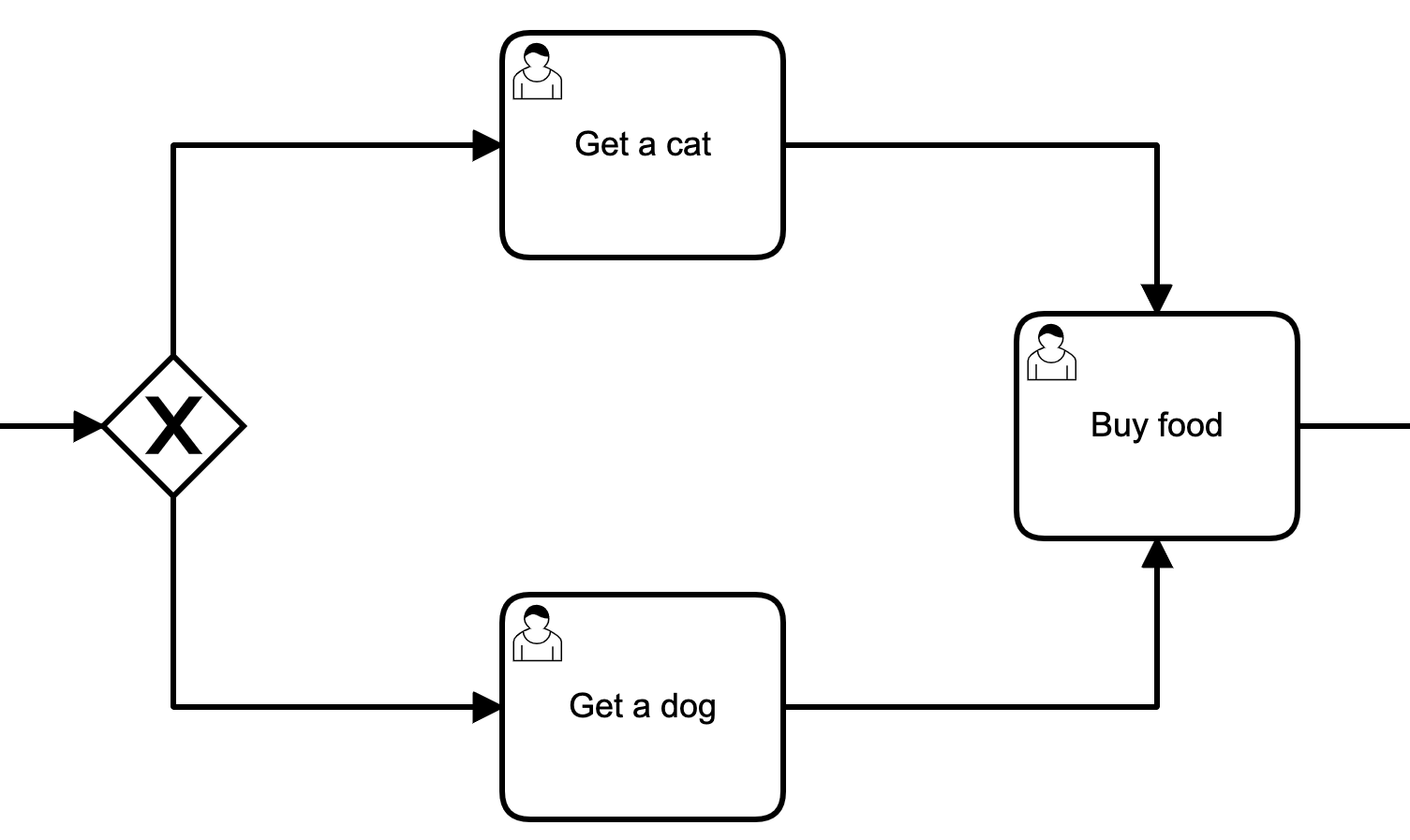
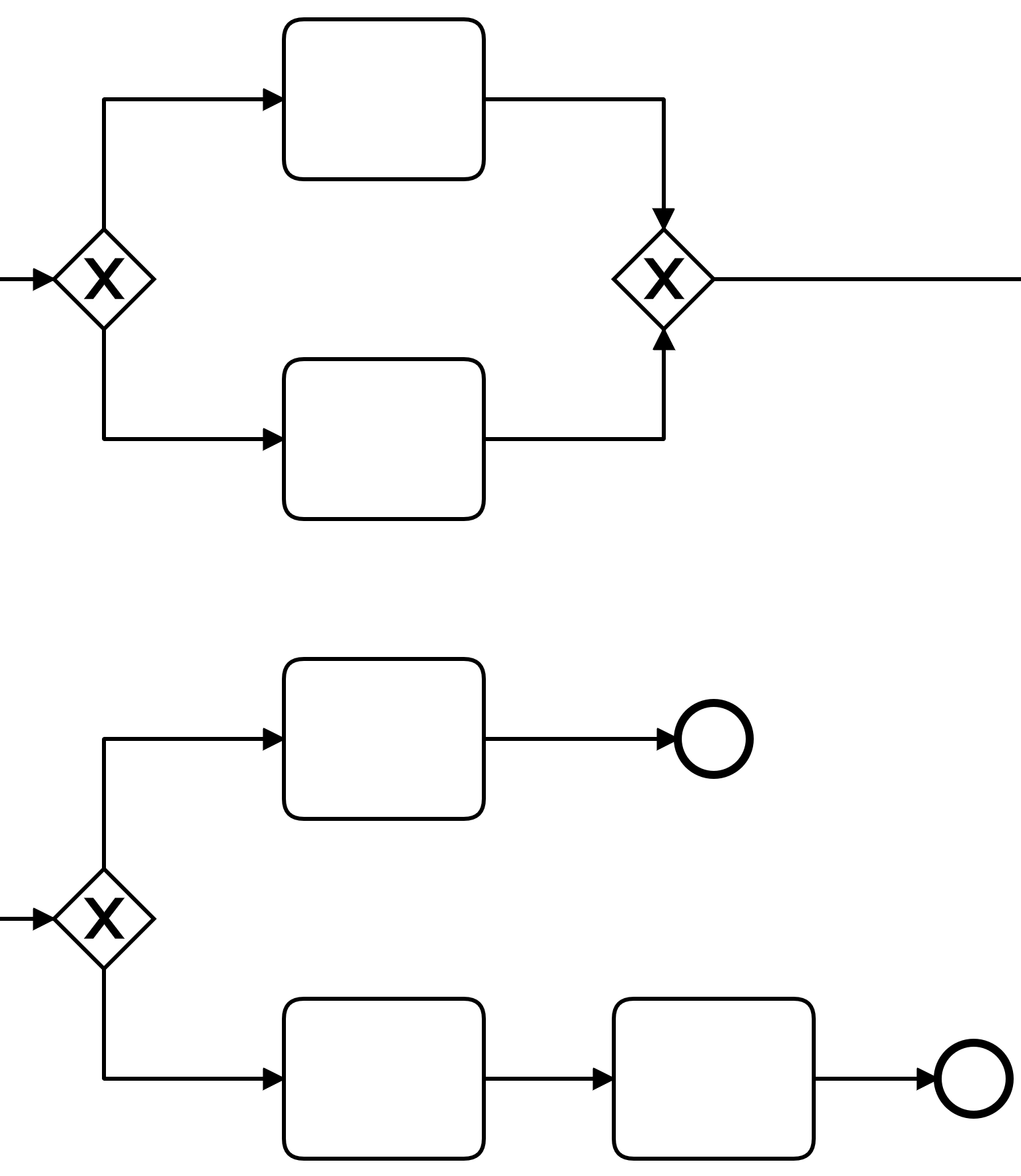
Exclusive Gateway
-
Handles mutually exclusive flows
-
Splitting behaviour
-
Gateway chooses exactly one outgoing flow for incoming flow
-
-
Merging behaviour
-
Gateway merges incoming flow into outgoing flow
-
Paths must not be merged
-
But all must reach end event to end process
-
-
Can be merged into activity implicitly
-
Process
-
Group of all activities, events and gateways including the flows between them
-
Defines a scope
-
Often invisible at global scope (i.e., the canvas)
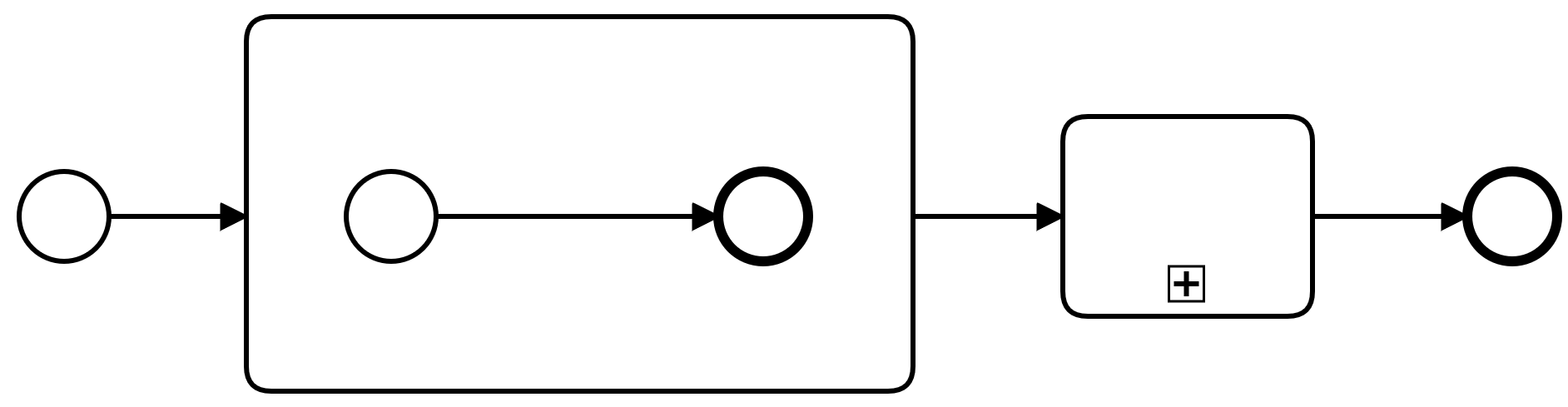
Subprocess
-
Defines scope within another process - can have boundary events[4]
-
Defined in the same file - lifecycle is bound to that of containing process
-
Segments the process into chunks or phases
-
Is a compound activity and follows the semantics for an activity
-
Can be displayed collapsed or expanded (tooling support varies)
-
Starts with a start event and ends with (at least one) end event