BPMN Level 1 Palette
part 2 - modelling common patterns
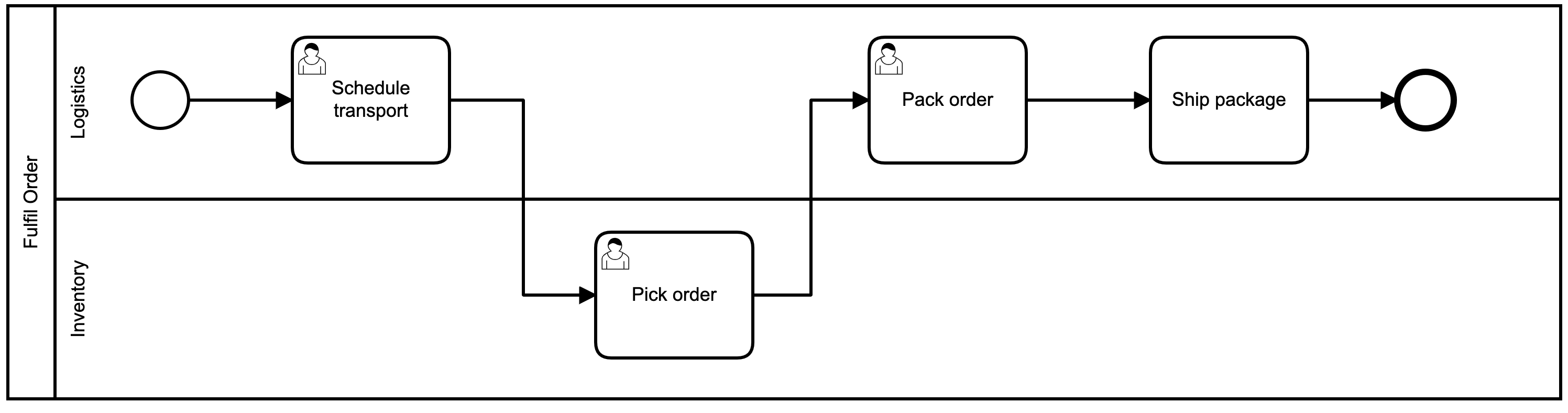
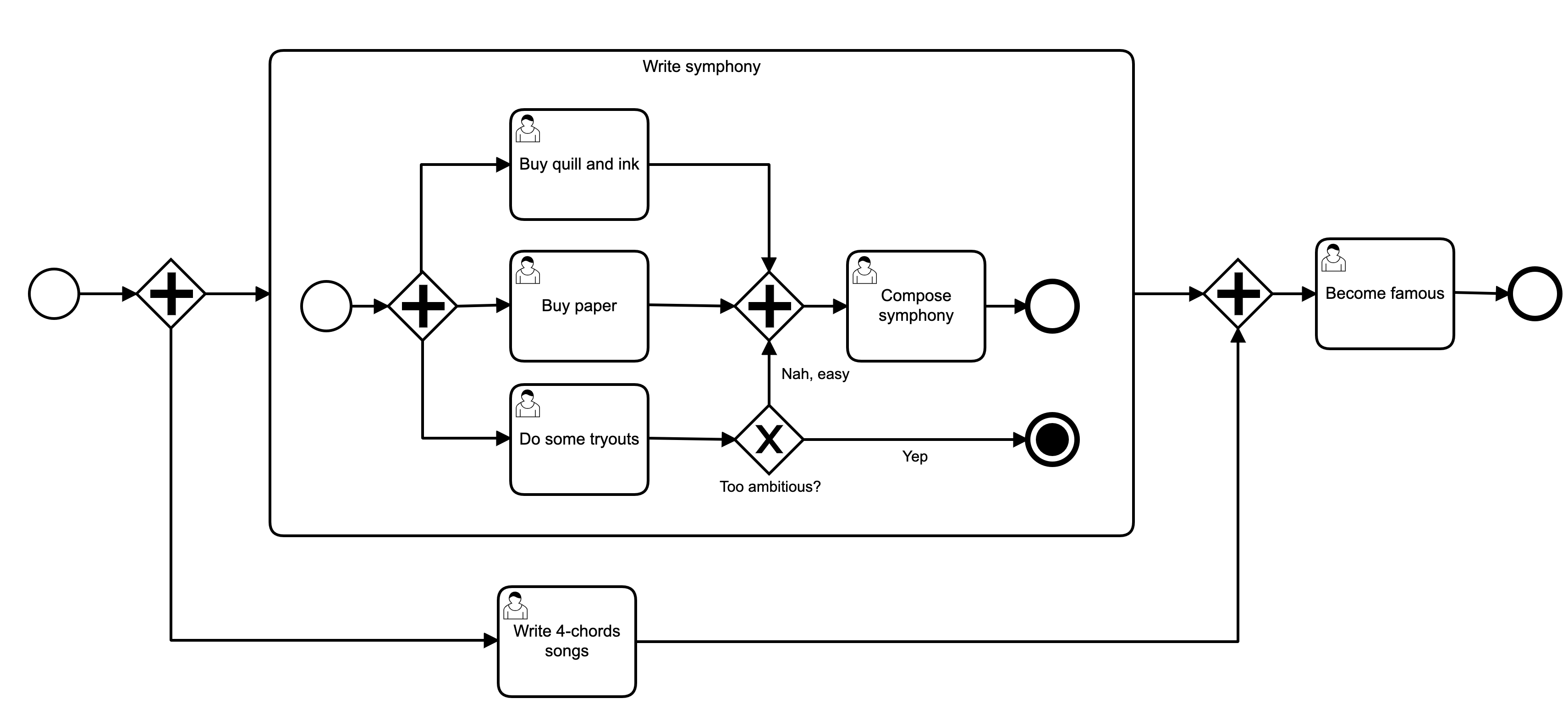
Pool and Lane
-
Pool represents a single participant: mostly a process
-
Lane represents the performer of an activity in the pool’s process
-
Typically a role or organisational unit
-
Mostly relevant to user tasks
-
-
Pools and Lanes are an optional way to show how control flow switches between responsible organisational units
-
Do not affect execution of the process
-
Can be used to show the communication of the process with the outside world
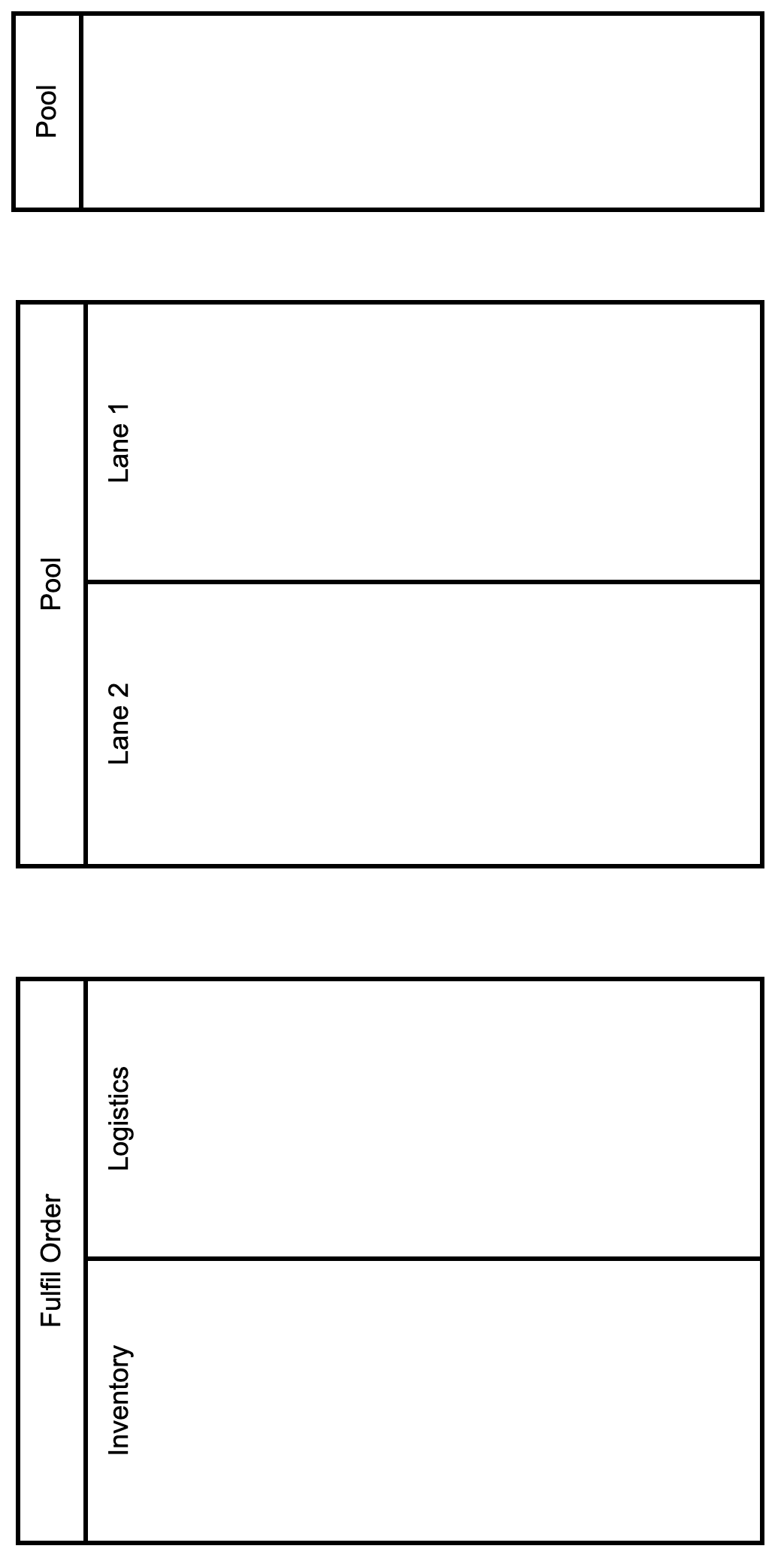
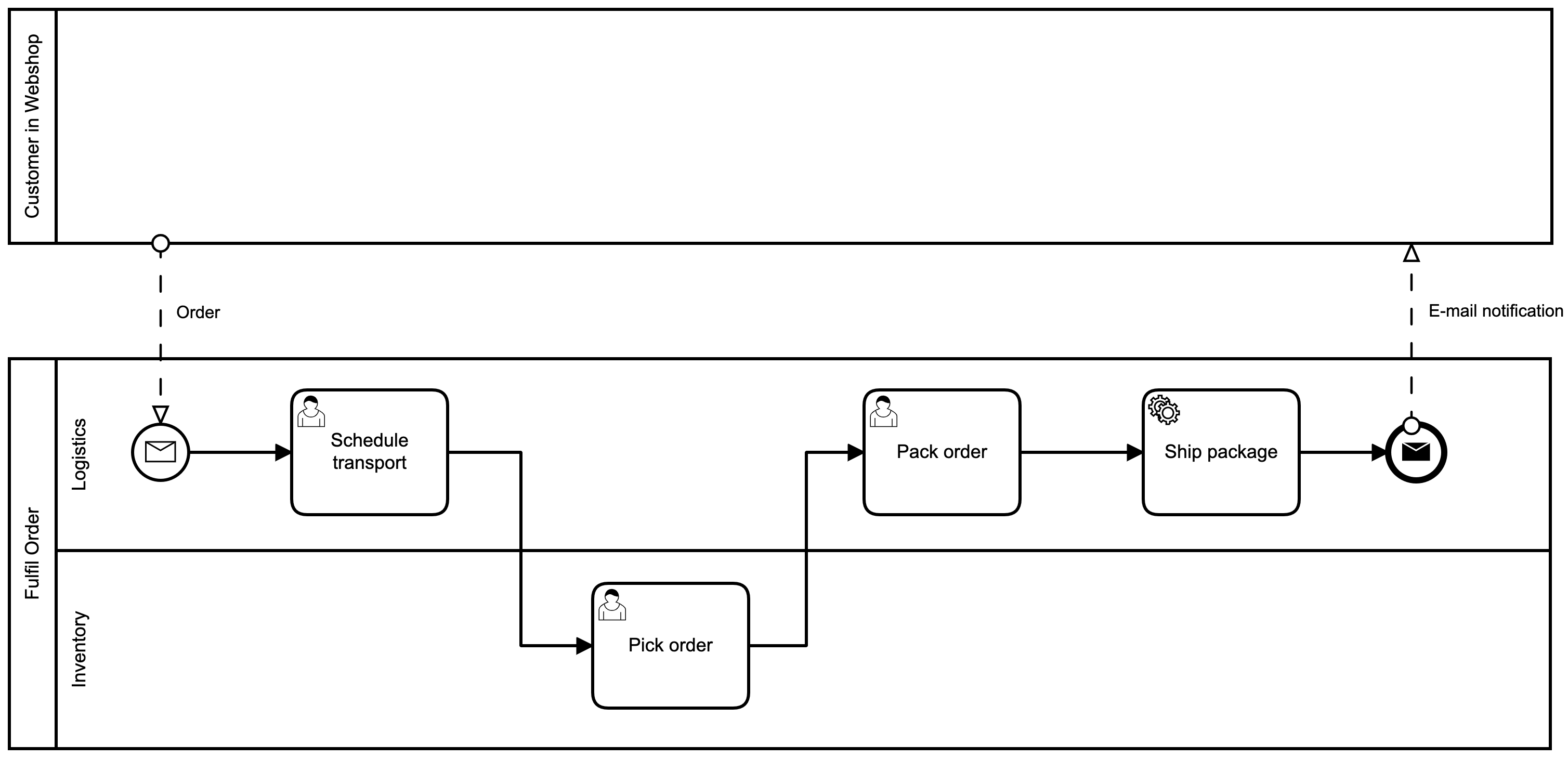
Message Flow
-
Messages represent communication of a process with any outside entity
-
Human or System
-
-
Not necessarily a technical message!
-
Can even represent a physical transfer
-
Messages flow between pools and their flow nodes, never inside pools
-
Message flow has one source and one target flow node
-
Can enter event or activity from any angle
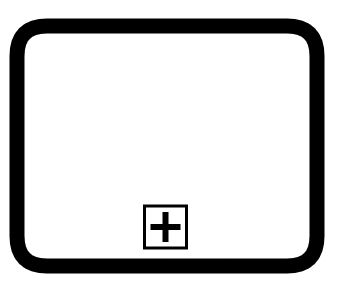
Call Activity
-
Use of a subprocess defined in separate model (file) - lifecycle is separated
-
Tooling support for navigation may vary
-
-
In process where called, drawn as a collapsed subprocess with thick border
-
Reusable to call from other processes
-
Process must complete before activity can complete
-
Or throw an exception (level 2)
-
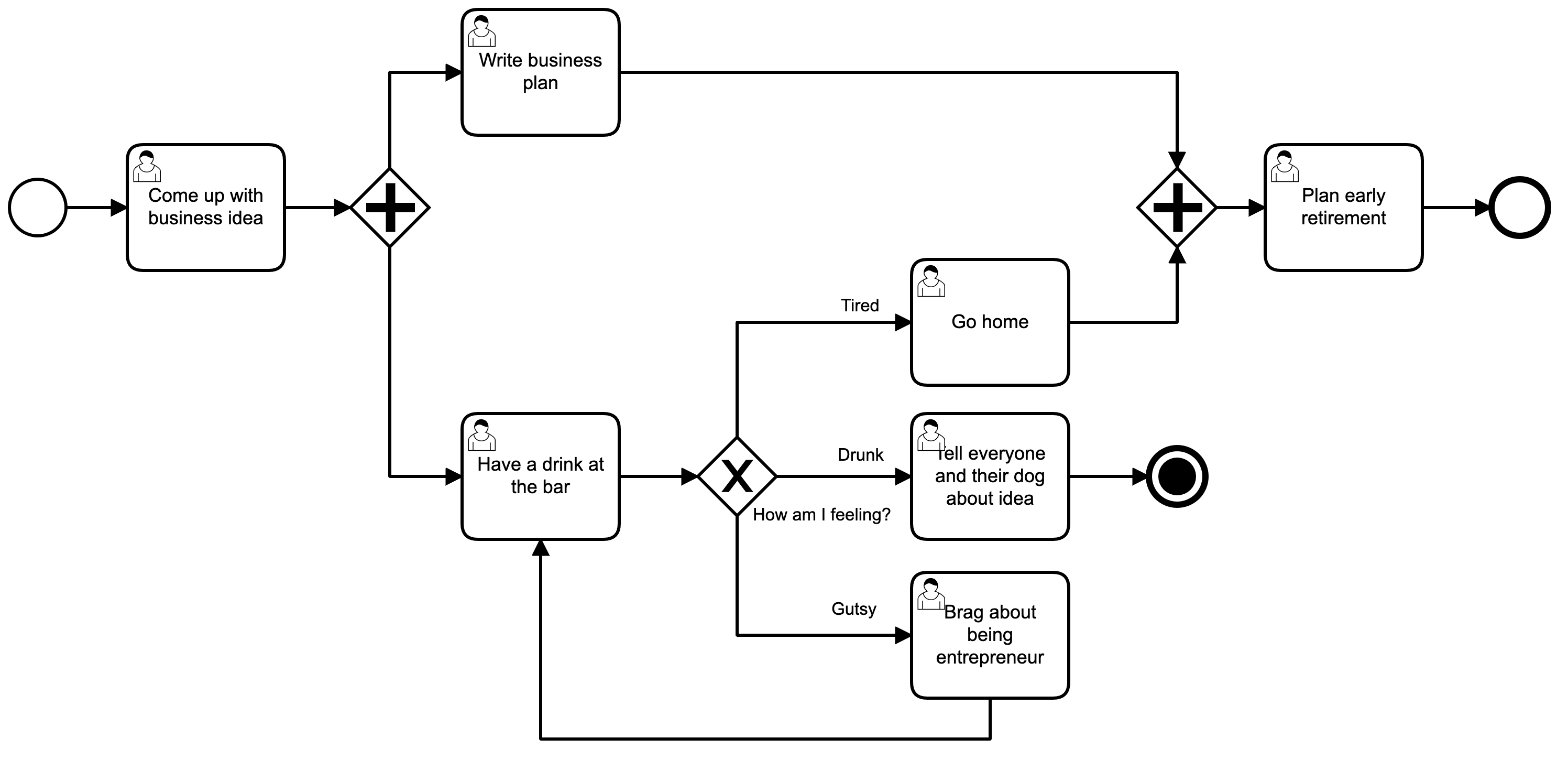
Terminate End Event
-
Terminates the current scope and its activities
-
Doesn’t always terminate the whole process!
-
Usually reached only conditionally
-
Execution continues on the normal flow from the containing process: no emission
-
Do not overuse: a regular end event is just as strong as a terminate
Documentation
-
Documents any element in the process model
-
Usage is optional and format is free to choose
-
Has no graphical depiction in the diagram
-
Has no effect on the execution
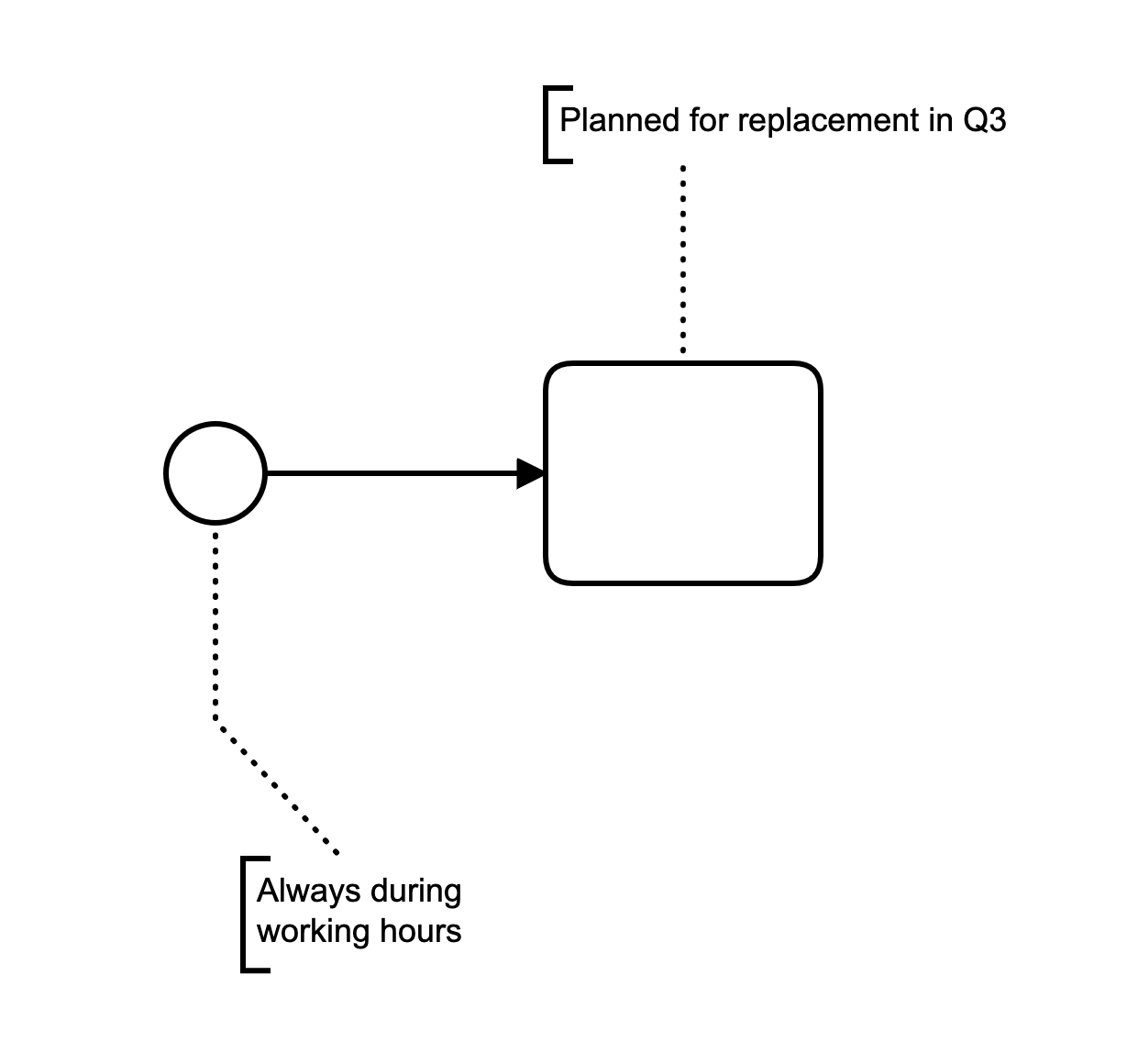
Text Annotation
-
Textual documentation with graphical depiction in diagram
-
Bound to a flow node by an association (dotted line)
-
Has no effect on the execution
Group
-
Graphical grouping of elements in a diagram
-
Displayed with a dashed border
-
Has no effect on the execution
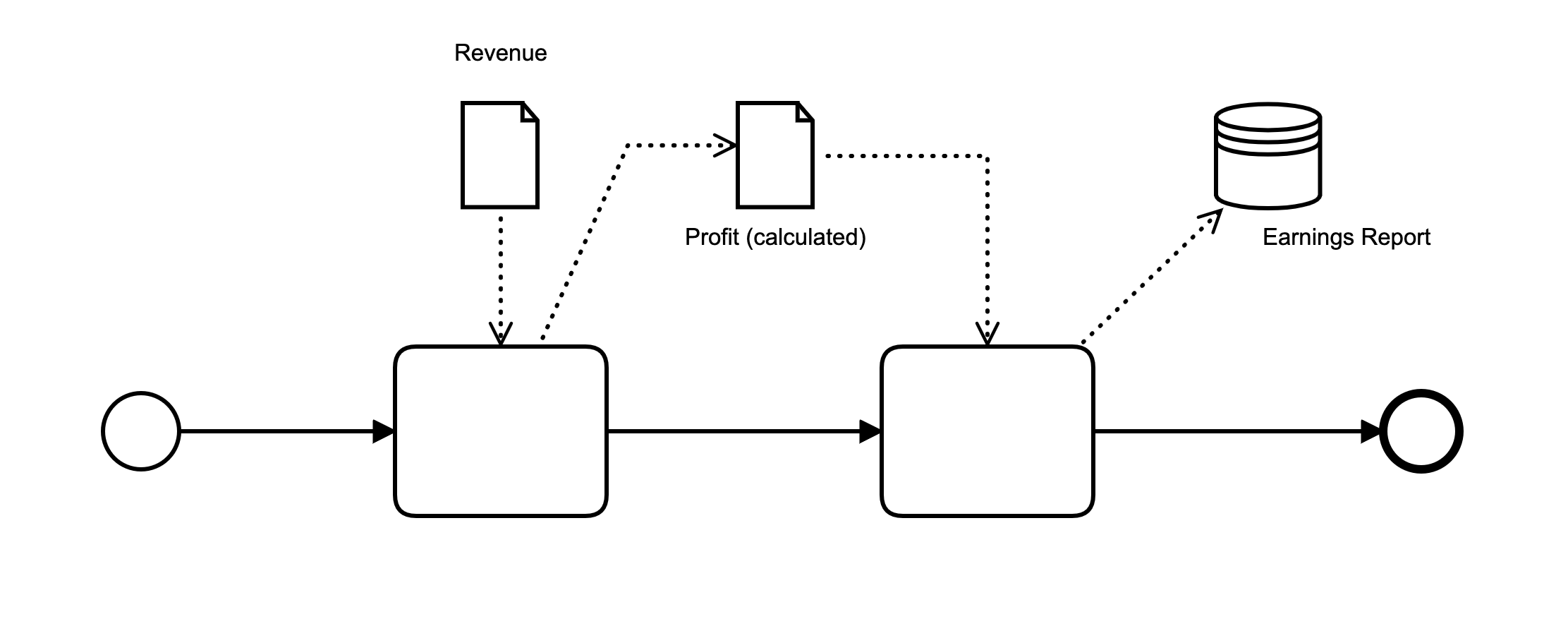
Data Object and Data Storage
-
Geared towards executable process model design
-
Linked to process elements with associations
-
Tooling support varies strongly for execution
-
-
Data object represents a piece of information local to the process instance (think of a variable)
-
Can be the input and/or output to a task or used in a gateway’s condition
-
State optionally in brackets
-
Only exists in the context of the process
-
-
Data storage represents persistent data for a piece of information
-
Think of a row in a database
-
Can be queried and updated from the process
-