Curl
The curl project provides two tools, the libcurl library and the curl command line tool.
The first is a client-side URL transfer library that supports a whole host of protocols.
The curl tool can be used for getting and sending data with a URL syntax and uses libcurl under the hood.
When you install curl, you get both tools and can use the curl command to perform requests and read the results.
We will use curl in some places to perform HTTP(s) calls, mostly to perform REST requests.
You will be provided with the basic commands you can copy and paste to use curl.
|
GUI Alternatives
If you prefer a GUI tool over a command line tool, Postman is one of the best-known ones. You can also install an extension to most browsers that will offer similar functionality - these are normally called REST Client or something similar. Yet Another REST Client is an example of an extension for Chromium based browsers. Most IDEs also have some functionality to perform requests and inspect the results. For VSCode, the REST Client extension is a good option. |
|
Formatting JSON
Many of the requests we’ll perform return JSON by default.
Reading JSON in plain text is a bit cumbersome, so there are additional tools you can use to improve the experience, if you want to.
One of those tools is jq.
Instead of the plain text output, the result is now coloured (and formatted, although this particular service already does that as a convenience), making it easier to read. 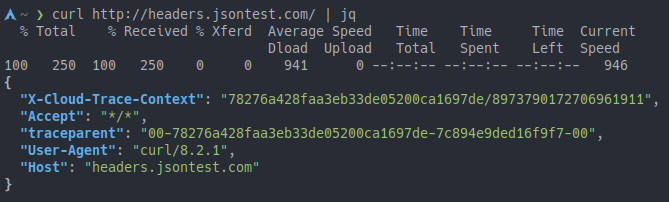
Figure 1. Example of JSON output formatted with
jqIf you want to, you can additionally install |
macOS
The curl program is pre-installed macOS.
Test whether you can use curl by going to your terminal application and run the following command.
$ curl -V
Note that the -V flag is a capital letter V.
You should see the version information of the curl program being printed.
curl -Vcurl 7.88.1 (x86_64-apple-darwin22.0) libcurl/7.88.1 (SecureTransport) LibreSSL/3.3.6 zlib/1.2.11 nghttp2/1.51.0
Release-Date: 2023-02-20
Protocols: dict file ftp ftps gopher gophers http https imap imaps ldap ldaps mqtt pop3 pop3s rtsp smb smbs smtp smtps telnet tftp
Features: alt-svc AsynchDNS GSS-API HSTS HTTP2 HTTPS-proxy IPv6 Kerberos Largefile libz MultiSSL NTLM NTLM_WB SPNEGO SSL threadsafe UnixSockets
If you get a message that the curl program cannot be found, install it first from the website or use a package manager like Homebrew to install it.
|
Check that you can access a URL with another curl command.
$ curl -I http://www.example.com
The result will be the HTTP headers returned by the website, if the command is successful.
curl -IHTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Encoding: gzip
Accept-Ranges: bytes
Age: 135913
Cache-Control: max-age=604800
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Date: Wed, 23 Aug 2023 06:55:00 GMT
Etag: "3147526947"
Expires: Wed, 30 Aug 2023 14:07:30 GMT
Last-Modified: Thu, 17 Oct 2019 07:18:26 GMT
Server: ECS (dcb/7ECA)
X-Cache: HIT
Content-Length: 648That’s it for curl!